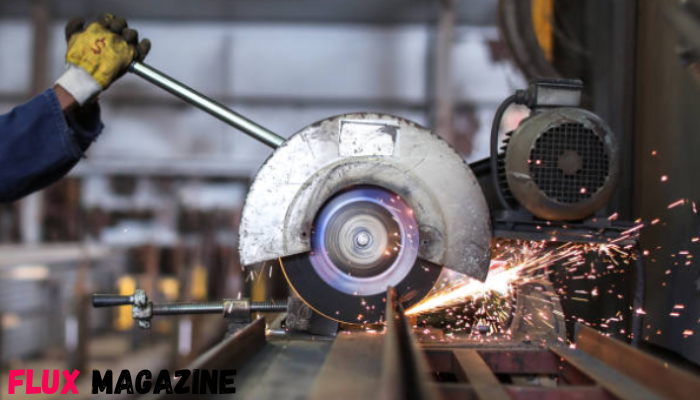
Modern manufacturing and production plants utilize industrial ovens for curing, drying, baking, and heat treating. Parts that stop functioning for any reason may cause significant production loss and delay shipments, thus increasing operational costs, operational efficiency loss and increasing costs. B2B businesses sustain operational efficiency by sourcing high-quality industrial hardware supplies and observing proper procedures replacing industrial oven parts. This article aims to shed light on the salient replacing components of industrial ovens while optimizing their performance over the long term and minimizing operational downtime.
The Role Of Industrial Oven Maintenance
Industrial ovens are subject to industrial conditions that are hostile, with respect to high temperatures, nonstop cycles, and contact with chemicals or particulate matter. Heating elements, thermocouples, fans, and insulation materials are prone to wear. Forming timely replacement cycles and preventative rollover strategies are the contact points that sustain productivity and operational efficiency over long periods Industrial hardware supplies also factor into these decisions.
In the case of B2B operations, production schedules can be thrown wildly off course by the loss of any single oven, or any single pipe such, for even a single hour. Adopting a systematic approach for these schedules protects sensitive products, enhances the overall safety of volatile scenarios for the users and improves overall worker safety.## Key Components That Require Regular Replacement
In every Technological Business Center (TBC), distinct components of every technological advancement that can lead to its dominance in a given field will become a central point of possible reduction of its failure. Some common parts of industrial ovens that can cause breakdowns include:
Heating elements: Components that are left unused for a long duration can burn out or become less functional due to efficiency loss. This in return can cause uneven heating to take place.
Thermal sensors and thermocouples: Accurate recordings of cure temperature and for sensor thermocouples can hold greatly damaging the product due to overheating or under heating.
Rotors and fans: Motors of the circulation fans are to make the heat in the oven to be uniformly dispersed. If the fans break then the oven will start developing cold or hot spots.
Seals and gaskets of door: Broken seals due to wear and tear make the oven consume more energy which increases the duration for the product to process due to heat loss.
Relays and control boards: These parts of the electronic oven are responsible for its functioning and control setting. If these parts break then there will be a stand still in production.
Being able to focus on these specific parts can greatly improve the ability to maintain a constant factory production that will be met.
Best Practices for Replacing Parts of an Industrial Oven
Replacing parts of an industrial oven is a process that could result in more downtime, so it is best that these steps be taken to minimize this phenomenon. The suggestions below can be applied to any business-to-business case.
Set Up a Schedule for Industrial Maintenance
Effective maintenance of an industrial oven entails some component inspection and some cleaning, so the overall time taken is referred to as the oven maintenance routine. Troubleshooting and planning procedures are simplified as many unforeseen breakdowns can be avoided and fixed in time. Keeping track of repair records and historical/ancient data is essential to predicting when parts are most likely to be in need of replacement.
Purchase Genuine Industrial Hardware Supplies
Purchasing genuine industrial hardware supplies is essential because several of these parts have inadequate performance to be able to support an oven, and consequently downtime.
Enhance Maintenance Staff Skills
Training maintenance staff is vital to the whole process of replacing a section of the oven. Employees are more likely to be amateurs in oven diagrams than any model that might be represented, but with the right materials and focus the most acceptable results can be achieved. The adverse effect of faulty equipment is mostly a result of improper maintenance.
Set Up a Staging Area with Sufficient Parts for Components
Having a stock inventory of parts for critical replacements can help lessen the amount of time lost. Also, when maintenance teams access a broken part, they can skip the time-consuming shipping and purchasing. Staging areas should be organized so that parts and tools of varying sizes and shapes can be found.
Outline Procedures for Replacement
Having precise replacement policies for each critical part enables the personnel to concentrate on the right processes. Documentation should cover a sequence of operations, ensure that essential safeguards are integrated, tools are supplied, and assistance is and can be provided. Well written procedures help eliminate mistakes and help increase the speed of repairs.
Reducing Replacement Downtime
Most broken parts are however still covered by the above prevention strategies. Companies should focus on minimizing the broken part’s impact on production.
Schedule replacements at a time that’s least busy: Where maintenance is needed and production is running, contributors should aim to make their processes synchronous.
Components should be easy to switch out: ovens that can have their heating parts, fans, and control units removed and replaced in a modular fashion are often more efficient.
Anticipate issues that can arise to above strategies: Finding factors that will complicate the planned replacement before the replacement happens can be beneficial.
Work Closely with the production division. The expectations for the length of the outage should be managed to ensure that operations are easy and uninterrupted.
Completing these oven maintenance operational strategies impact optimization while preserving product quality.
Specialized Equipment Considerations
Some industrial ovens in research labs, precision manufacturing, or environmental testing, for example, may need specific equipment. Parts for environmental chamber parts, for example, are rarely produced without specific, stringent guidelines regarding humidity control, temperature variation, and contamination control. The use of these parts for B2B environments, however, calls for precision in meeting compliance and operational dependability.
Condition monitoring systems combined with predictive maintenance also help anticipate unexpected failures. Component health KPI systems combined with predictive analytics can alert maintenance for replacement, narrowing excess oven operational periods. Identifying critical parts for replacement and replacement during sinks are essential to oven investment microeconomics in ROI.
Conclusion
In B2B environments that use industrial ovens, efficient, rapid part replacement during maintenance conserves operational, cost, and quality workflows. Best practices of preventive maintenance scheduling, acquiring maintenance industrial hardware supplies, maintenance team training, critical part replacement boarding, and thorough procedure documentation ensure timely part replacements.
This detail on specialized plus environmental convection ovens stresses the need for the quality and compliant parts. Along with reducing downtime and extending equipment life, applying proactive maintenance approaches and high quality spare parts enhances profitable production while ensuring equipment availability. In competitive industrial setups, sprinting replacements of industrial oven parts is more than just a maintenance operation, it’s a cornerstone for sustaining manufacturing excellence.
















Show Comments (0)